PON is the passive optical network with a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) structure, while GPON is the gigabit PON defined by the ITU-T G.984.x series standards, which is also one of the PON technologies. The following GPON features meet carriers' higher requirements on transmission distance, bandwidth, reliability, and low operation costs:
Longer transmission distance: GPON uses optical fibers to transmit data and its coverage radius at the access layer can reach 60 km. Therefore, it can solve the contradiction between distance and bandwidth of twisted pairs.
Higher bandwidth: Each GPON port supports the downstream and upstream rates of up to 2.5 Gbit/s and 1.25 Gbit/s respectively. It meets users' requirements on high-bandwidth services, such as HD TV and live broadcast.
Flexible full-service experience offered by Quality of Service (QoS): QoS controls traffic for different users and user services, ensures multi-service bandwidth for multiple users, and provides differentiated services based on different user services.
Optical splitting: A single fiber in the central office is divided into multiple drop fibers with the help of an optical splitter. The optical split ratio of 1:128 is supported. In this way, GPON saves backbone fiber resources and reduces O&M costs.
Adopting the ATM encapsulation mode, BPON is mainly used for carrying ATM services. With the obsolescence of the ATM technology, BPON also drops out. EPON is an Ethernet passive optical network technology. GPON is a gigabit passive optical network technology and is to date the most widely used mainstream optical access technology. GPON is defined by ITU-T Recommendation G.984.x.
GPON network architecture is as follows:
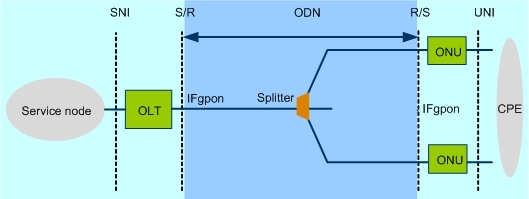
IFgpon: GPON interface
SNI: Service Node Interface
UNI: User to Network Interface
CPE: Customer Premises Equipment
Hope this help.
Learn more:
What are default username and passwords for logging into an ONT?



















































































































