What is Firewall
Firewalls were invented by the founder of Check Point Gil Shwed in 1993 and introduced to the Internet (US5606668 (A) 1993-12-15). It is a network security system located between the internal network and the external network.
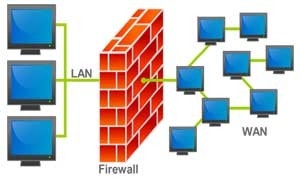
The Firewalls are generated by people’s need for security of network. Whether the packet can arrive correctly, the arrival time, direction, etc. is not the focus of the firewall, the focus is whether the packet should be passed, after the network will cause harm.
The fundamental purpose of the firewall is to ensure that any non-permitted packets are “not valid”.
History
The firewalls developed from first generation to third generation.
First generation: packet filters
The first reported type of network firewall is called a packet filter. Packet filters look at network addresses and ports of packets to determine if they must be allowed, dropped, or rejected. The first paper published on firewall technology was in 1988, when engineers from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) developed filter systems known as packet filter firewalls. This fairly basic system is the first generation of what later became a highly involved and technical Internet security feature. At AT&T Bell Labs, Bill Cheswick and Steve Bellovin continued their research in packet filtering and developed a working model for their own company based on their original First Generation architecture.
Second generation: "stateful" filters
From 1989–1990 three colleagues from AT&T Bell Laboratories, Dave Presotto, Janardan Sharma, and Kshitij Nigam, developed the second generation of firewalls, calling them circuit-level gateways.
Second-generation firewalls perform the work of their first-generation predecessors but operate up to layer 4 (transport layer) of the OSI model. This is achieved by retaining packets until enough information is available to make a judgement about its state. Known as stateful packet inspection, it records all connections passing through it and determines whether a packet is the start of a new connection, a part of an existing connection, or not part of any connection. Though static rules are still used, these rules can now contain connection state as one of their test criteria.
Certain denial-of-service attacks bombard the firewall with thousands of fake connection packets in an attempt to overwhelm it by filling its connection state memory.
Third generation: application layer
Marcus Ranum, Wei Xu, and Peter Churchyard developed an application firewall known as Firewall Toolkit (FWTK). In June 1994, Wei Xu extended the FWTK with the kernel enhancement of IP filter and socket transparent. This was known as the first transparent application firewall, released as a commercial product of Gauntlet firewall at Trusted Information Systems. Gauntlet firewall was rated one of the top firewalls during 1995–1998.
The key benefit of application layer filtering is that it can "understand" certain applications and protocols (such as File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Domain Name System (DNS), or Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)). This is useful as it is able to detect if an unwanted application or service is attempting to bypass the firewall using a protocol on an allowed port, or detect if a protocol is being abused in any harmful way.
As of 2012, the so-called next-generation firewall (NGFW) is nothing more than the "wider" or "deeper" inspection at application stack. For example, the existing deep packet inspection functionality of modern firewalls can be extended to include:
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- User identity management integration (by binding user IDs to IP or MAC addresses for "reputation")
- Web application firewall (WAF). WAF attacks may be implemented in the tool "WAF Fingerprinting utilizing timing side channels" (WAFFle) Next-Generation Firewalls
Hot Brands of Firewalls
Cisco Firewalls
Cisco Firewalls can provide your network effective detection and security protection. The products family includes a variety of firewalls to meet the different demands of any size of business. There are various series:
1. ASA 5500-X with FirePOWER Services
The ASA 5500-X Series, the industry’s first threat-focused next-generation firewall (NGFW), will help you stop more threats.
2. Cisco ASA 5500-X Series Firewalls
Deliver a robust suite of highly integrated, market-leading security services for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), enterprises, and service providers.
3. Cisco Small Business ISA500 Series
The ISA500 Series contains ISA550, ISA550W, ISA570, and ISA570W. This product is no longer being sold and might not be supported (End-of-Life and End-of-Sale).
Huawei Firewalls
Huawei Security is pioneering a securely connected world and an open eco-system. Router-switch.com provides Huawei Next-Generation Firewalls, Huawei Application Security Gateways, Huawei DDoS Protection Systems, Huawei Data Center Firewalls, Huawei Security Platforms, Huawei Firewall Security Modules, Huawei Security Licenses and Huawei Firewall Security Accessories to build reliable and secure networks. There are various categories:
1. Huawei Next-Generation Firewalls
Huawei NGFWs are designed for network egresses of medium-sized businesses or branch offices of large enterprises, large data centers, cloud service providers, and large-scale enterprise campus environments.
2. Huawei DDoS Protection Systems
Provide non-stop protection against hundreds of DDoS attacks for carriers, large-scale enterprises, Internet data centers, and ISPs.
3. Huawei Application Security Gateways
NIP2000D/5000D Series are designed to detect threats to traffic and applications in enterprise, IDC, and campus networks. The SVN5800 Series provides safe and secure remote access for mobile devices, branch interconnections, cloud access.



















































































































