A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks.
Router is connected to the network in the LAN or WAN equipment. It will automatically select and set the route according to the channel to the best path, in order to send the signal.
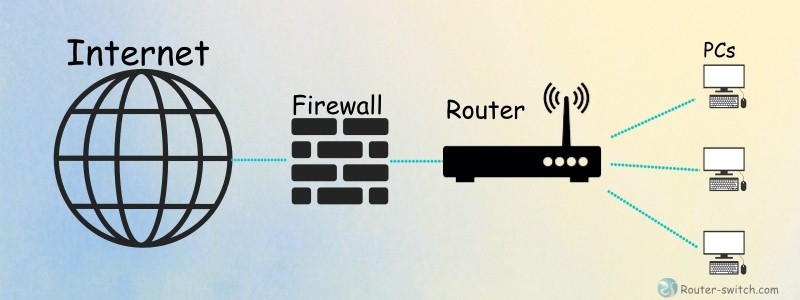
In other word, Router is the hub of the Internet, "a traffic police."
How many Types of Routers?
There are three types of routers in the market. These types are the main categories.
(1) Broadband Routers
Broadband routers can do different types of things. Broadband routers can be used to connect computers or to connect to the Internet.
If you connect to the internet through phone and using Voice over IP technology (VOIP) then you need broadband router. These are often a special type of modem (ADSL) that will have both Ethernet and phone jacks.
(2) Wireless Routers
Wireless routers create a wireless signal in your home or office. So, any PC within range of Wireless routers can connect it and use your Internet.
In order to secure your Wireless routers, you simply need to come secure it with password or get your IP address. Then, you'll log on into your router with the user ID and passwords will that come with your router.
(3) Other Types of Routers
Ⅰ. Edge Routers
This type of router is placed at the edge of the ISP network, that is normally configured to external protocol like BGP (Border gateway protocol) to another BGP of other ISP or large organization.
Ⅱ. Subscriber Edge Routers
This type of router belongs to an end user (enterprise) organization. It’s configured to broadcast external BGP to its provider’s AS(s)
Ⅲ. Inter-provider Border Routers
This type of router is for Interconnecting ISPs. This is a BGP speaking router that maintains BGP sessions with other BGP speaking routers in other providers' ASes.
Ⅳ. Core Routers
A router that resides within the middle or backbone of the LAN network rather than at its periphery. In some instances, a core router provides a stepdown backbone, interconnecting the distribution routers from multiple building of a campus (LAN), or Large Enterprise Location (WAN). They tend to be optimized for a high bandwidth.
Ⅴ. Wired and Wireless Routers
Home and small office networking is becoming popular by day by the use of IP wired and wireless router. Wired and wireless router are able to maintain routing and configuration information in their routing table. They also provide the service of filtering traffic of incoming and outgoing packets based on IP addresses.
Some wireless routers can be combined the functions of router with those of a network switch and that of a firewall in one.



















































































































