In computer networking, The layered concept of networking was developed to accommodate changes in technology. Each layer of a specific network model may be responsible for a different function of the network. Each layer will pass information up and down to the next subsequent layer as data is processed.
The OSI( Open System Interconnection) Network Model Standard
The OSI network model layers are arranged here from the lower levels starting with the physical (hardware) to the higher levels.
The 7 layers of OSI
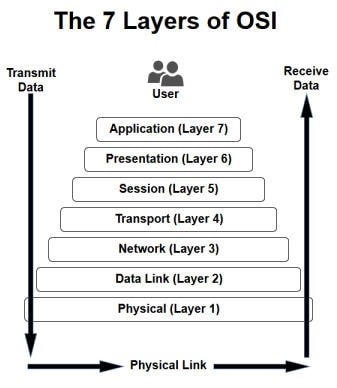
Figure from webopedia
- Physical Layer
An application that communicates with other computers that corresponds to the application's communication service.
- Data Link Layer
It defines how to transfer data on a single link
- Network Layer
This layer defines the end-to-end packet transport, which defines the logical addresses that identify all nodes and also defines how the routes are implemented and how they are learned.
- Transport Layer
The functions of this layer include whether to choose the error recovery protocol or the error-free recovery protocol, and multiplex the input of different application data streams on the same host, and also include the function of reordering received packets that are not in the correct sequence.
- Session Layer
It defines how to start, control and end a session, including the control and management of multiple bidirectional messages so that applications can be notified when only a portion of a continuous message has been completed, so that the data seen by the presentation layer is contiguous, In some cases, if the presentation layer has received all of the data, the data represents the presentation layer.
- Presentation Layer
The main function of this layer is to define the data format and encryption.
- Application Layer
An application that communicates with other computers that corresponds to the application's communication service.
What is session layer?
The session layer is the fifth layer of the OSI model. Based on the transport layer, session layer uses the services provided by the transport layer, enables applications to establish and maintain sessions and to synchronize sessions. The use of checkpoints by the session layer enables the communication session to resume communication from the checkpoint at the time of communication failure. This ability to send large files is extremely important.
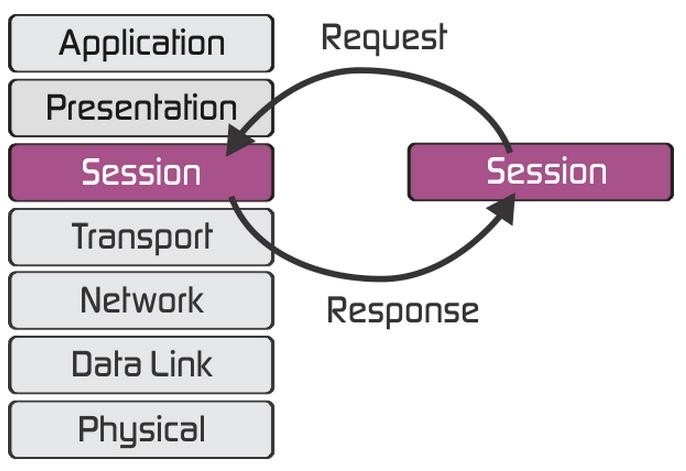
Figure from fiberbit.com
Session layer functions
- Establish a connection between the session entities
In order to establish a session connection for two peer session service users, several things should be done as follows.
- Map the session address to the shipping address.
- Select the required transport quality of service(QOS) parameters .
- Negotiate the session parameters.
- Identify each session connection.
- Transmit limited transparent user data.
- Data transfer phase.
This stage is to realize the organized and synchronous data transmission between two session users, where the user data unit is the SSDU and the protocol data unit is the SPDU, and the data transmission between the session users is performed by converting the SSDU into the SPDU.
- Connection release
Connection release is through the "ordered release", "discarded", "limited transparent user data transfer" and other functional units to release the session connection.
Session-Level Standards In order to enable functional negotiation during the session establishment phase and to facilitate reference and reference by other international standards, twelve functional units are defined. Each system can be based on its own circumstances and needs, based on the core functional service unit, matching other functional units to form a reasonable subset of session services.
Session layer protocols
The table shows the popular Session Layer Protocols
|
Item |
Stands for |
|
ADSP |
AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol |
|
ASP |
AppleTalk Session Protocol |
|
H.245 |
Call Control Protocol for Multimedia Communication |
|
ISO-SP |
OSI session-layer protocol (X.225, ISO 8327) |
|
iSNS |
Internet Storage Name Service |
|
L2F |
Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol |
|
L2TP |
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol |
|
NetBIOS |
Network Basic Input Output System |
|
PAP |
Password Authentication Protocol |
|
PPTP |
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol |
|
… |
… |

Expertise Builds Trust
20+ Years • 200+ Countries • 21500+ Customers/Projects
CCIE · JNCIE · NSE7 · ACDX · HPE Master ASE · Dell Server/AI Expert




















































































































