Most operators will initially integrate 5G networks with existing 4G networks to provide a continuous connection.
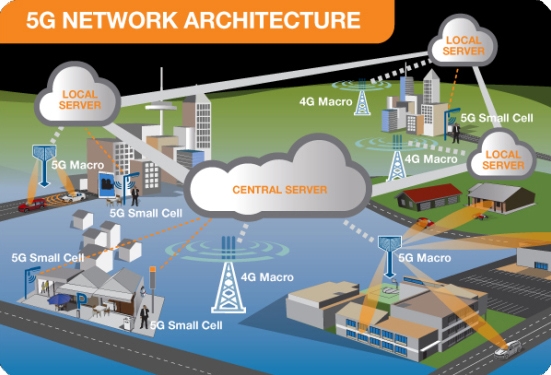
5G network architecture illustrating 5G and 4G working together, with central and local servers providing faster content to users and low latency applications.
A mobile network has two main components, the 'Radio Access Network' and the 'Core Network'.
The Radio Access Network - consists of various types of facilities including small cells, towers, masts and dedicated in-building and home systems that connect mobile users and wireless devices to the main core network.
Small cells will be a major feature of 5G networks particularly at the new millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies where the connection range is very short. To provide a continuous connection, small cells will be distributed in clusters depending on where users require connection which will complement the macro network that provides wide-area coverage.
5G Macro Cells will use MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) antennas that have multiple elements or connections to send and receive more data simultaneously. The benefit to users is that more people can simultaneously connect to the network and maintain high throughput. Where MIMO antennas use very large numbers of antenna elements they are often referred to as 'massive MIMO', however, the physical size is similar to existing 3G and 4G base station antennas.
The Core Network - is the mobile exchange and data network that manages all of the mobile voice, data and internet connections. For 5G, the 'core network' is being redesigned to better integrate with the internet and cloud based services and also includes distributed servers across the network improving response times (reducing latency).
Many of the advanced features of 5G including network function virtualization and network slicing for different applications and services, will be managed in the core. The following illustration shows examples of local cloud servers providing faster content to users (movie streaming) and low latency applications for vehicle collision avoidance systems.
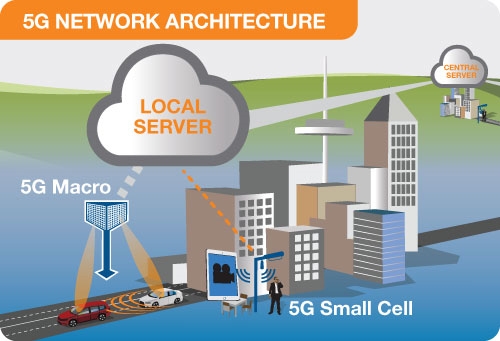
Example of a local server in a 5G network providing faster connection and lower response times
Network Slicing – enables a smart way to segment the network for a particular industry, business or application. For example emergency services could operate on a network slice independently from other users.
Network Function Virtualization (NVF) - is the ability to instantiate network functions in real time at any desired location within the operator's cloud platform. Network functions that used to run on dedicated hardware for example a firewall and encryption at business premises can now operate on software on a virtual machine. NVF is crucial to enable the speed efficiency and agility to support new business applications and is an important technology for a 5G ready core.
Learn more:
OPPO Reno3 5G Phone vs. Vivo iQOO Neo 5G Phone
Huawei P40 5G Phone vs. Huawei Mate 30 5G Phone
Kirin 990 vs. Snapdragon 855 and 855 Plus
What will happen to 4G phones when 5G comes?



















































































































