Wireless local area networking, also known as WLAN or wireless LAN, is a term for using wireless digital signals to connect computers and other devices. One of the most common wireless LAN technologies now in use is Wi-Fi, which refers to a set of standards for how devices can talk to each other on wireless networks. It's not the only wireless LAN technology out there, but it's the one you're most likely to encounter.
1.What is WLAN?
When you hear the term "wireless," it doesn't necessarily mean a device with no wires at all. The word originally applied to radios, which were often plugged into the wall or wired to batteries and also had wires internally.
Rather, the term means that the devices communicate without needing to be wired together. Radio was originally a wireless alternative to the wired telegraph, and wireless phones began as alternatives to traditionally wired landline phones.
In the context of computers and smart devices, wireless means that they can talk to each other digitally without having to be connected with wired technologies like Ethernet cables or dial-up modems that speak across the landline phone system. A local area network, or LAN, is any system that allows digital devices in a small geographic area, or even inside a building, to talk to each other. Many LANs nowadays are also connected to a wide area network and often ultimately to the internet.
A wireless LAN is any network that lets computers talk to each other without having to be wired to each other. This can be useful for reducing clutter in a home or office and for making it possible to move devices like smart phones and laptops around without loss of network connections or having to stretch wires from place to place.
2.What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is the wireless standard 802.11 and nothing else. Through the years, we've seen different evolutions of Wi-Fi, culminating in the new 802.11ax standard. Each version of the 802.11 standard is written for compatibility with 802.3 Ethernet -- the most common LAN type -- given that Wi-Fi typically extends the edge of the LAN.
Access points (APs) act as Layer 2 bridges between 802.11 and 802.3 standards in enterprise networks, and our wireless routers at home have an AP built in under the hood.
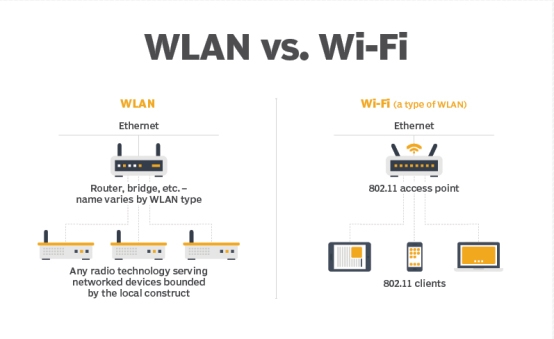
3.Wi-Fi vs. Wireless LAN
Wi-Fi networks are absolutely WLANs. But the important nuance is Wi-Fi is not the only type of WLAN. It's safe to say Wi-Fi is pretty much the only WLAN these days that services human clients directly, although in-building cellular may qualify as well, while most other WLANs likely service headless client device nodes.
Hope it help.
By the way, you can check the price of the 5G Wi-Fi router: Huawei 5G CPE Pro and Huawei 5G CPE Pro2.
What is WLAN?
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) is a network that does not require wired connections to connect devices within a limited area, such as a home or office. Common wireless network standards include Wi-Fi.
How does WLAN work?
WLAN uses radio waves to transmit data between devices. A router or access point (AP) broadcasts the network signal to wireless devices in the area, which then connect to the network via the wireless signal.
What is the difference between WLAN and Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a specific implementation of WLAN technology. WLAN is the general technology, while Wi-Fi is a commercial name for wireless network technology based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. Typically, Wi-Fi is used as a synonym for WLAN.
How can I improve WLAN signal strength?
Placement: Place the router in a central location, avoiding physical obstacles (like walls) and sources of interference (like microwave ovens).
Channel Adjustment: Choose less crowded wireless channels.
Upgrade Hardware: Use routers that support newer Wi-Fi standards (such as Wi-Fi 6).
Use Extenders: Add Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters to extend coverage.
How can I ensure WLAN security?
Change Default Passwords: Modify the default administrator password for the router.
Use Strong Passwords: Set a complex Wi-Fi password and use WPA3 or WPA2 encryption protocols.
Hide SSID: Disable SSID broadcasting to prevent unauthorized users from discovering the network.
Regularly Update Firmware: Keep the router’s firmware updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
What are WLAN frequency bands, and how should I choose?
WLAN typically operates on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 2.4 GHz band has a wider coverage range but is more prone to interference, while the 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference but has a shorter range. Many modern routers support dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) and you can choose the appropriate band based on your needs.
Why is my WLAN connection slow?
Interference: Other wireless devices (such as Bluetooth devices or microwave ovens) may interfere with the Wi-Fi signal.
Distance: The device might be too far from the router or there may be obstacles.
Bandwidth Usage: Network bandwidth might be used up by multiple devices simultaneously.
Router Performance: An older or lower-spec router may not provide adequate speed.
How can I troubleshoot WLAN connection issues?
Restart Devices: Try restarting the router and connected devices.
Check Settings: Ensure wireless network settings are correct and the password is entered correctly.
Check Signal Strength: Ensure the device is within the router’s coverage area.
Update Drivers: Make sure the wireless network adapter drivers are up to date.
What is WLAN Network?
A WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) is a wireless network that allows devices to connect and communicate within a limited area, such as a home or office, using radio signals and Wi-Fi technology.
What is WLAN Hotspot?
A WLAN hotspot is a location or device that offers wireless internet access via Wi-Fi, enabling devices to connect to the internet without cables, commonly found in public spaces like cafes and airports.
What Does WLAN Stand For?
WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network, a network that uses radio waves to connect devices wirelessly within a localized area, typically using Wi-Fi technology.
How to Connect WLAN to PC?
To connect WLAN to a PC, enable the Wi-Fi adapter, select the network from available options, click "Connect," and enter the password if required, ensuring WLAN network settings are correctly configured.
What Does WLAN Mean?
WLAN means Wireless Local Area Network. It is a network technology for wireless communication within a specific area, such as a home or office, using Wi-Fi to connect devices.
How to Crack WLAN Password?
Cracking a WLAN password is illegal and unethical. It involves unauthorized access to a wireless network, violating privacy and legal standards. Focus on using secure passwords for your own WLAN.
How to Find WLAN IP Address?
To find a WLAN IP address, access your router’s settings via a web browser using the default IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Navigate to network settings or status to view the WLAN IP address.
Where is WLAN on iPhone?
On an iPhone, WLAN settings are under "Settings" > "Wi-Fi," where you can toggle Wi-Fi on/off, select networks, and enter passwords. Manage your wireless connections from this section.
How to Use WLAN Direct?
WLAN Direct enables direct wireless connections between devices. To use it, ensure both devices support the feature, go to "Settings" > "Wi-Fi," select "Wi-Fi Direct" or similar, and follow the prompts.
What is WLAN on Printer?
WLAN on a printer refers to its capability to connect to a wireless network via Wi-Fi, allowing it to receive print jobs from devices on the same WLAN without needing a physical connection.
How to Turn On WLAN on Android?
To turn on WLAN on an Android device, go to "Settings" > "Network & Internet" > "Wi-Fi," and toggle the switch to enable Wi-Fi. Select a network and enter the password to connect to your WLAN.
How to Turn On WLAN on iPhone?
To enable WLAN on an iPhone, go to "Settings" > "Wi-Fi," and toggle the switch to turn Wi-Fi on. Your device will search for available networks for you to connect to your desired WLAN.
What is a WLAN Network?
A WLAN network is a Wireless Local Area Network that uses radio waves to connect devices within a specific area, such as a home or office, allowing for wireless internet and communication.
Where is WLAN on Android?
On an Android device, WLAN settings are located under "Settings" > "Network & Internet" > "Wi-Fi," where you can enable Wi-Fi, view available networks, and connect to your WLAN.
What Are WLAN Settings?
WLAN settings include options for configuring a wireless network, such as network name (SSID), security protocol (e.g., WPA2), password, and IP address settings, accessible through a router’s interface.
Learn More:



















































































































