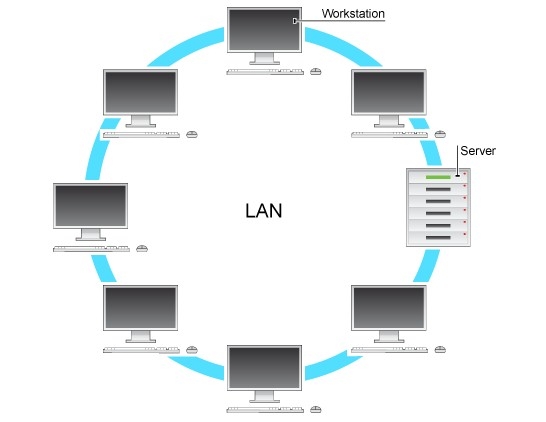
Local Area Networks (LAN) is widely used to share resources and exchange information by connecting personal computers and workstations in company office and factories.
A LAN covers a small area such as one site or building, eg a school or a college.
In a LAN, computers and hardware such as printers can be connected by cable (copper wiring), fibre optic cabling (glass fibres) or using a wireless (radio waves) connection.
Advantages of LANs:
- Hardware such as printers can be shared so individual workstations do not need their own printer. When they print, the data is stored in a queue on a server. The data is then passed to the printer.
- All the users work can be stored in a central place (the dedicated file server) so a user can access their work through any computer on the network.
- Software can be shared, software packages are stored on the server and downloaded to workstations as requested. Note that a licence still has to be bought for each copy of the software needed.
- Data can be shared because database files stored in the server are available to users around the network; data from CD-ROMs can also be shared across the network.
- Central back-up can take place automatically at regular intervals. A user will usually be able to retrieve work that has been deleted by mistake.
- Messages can be sent to people working at other computers on the network which can save time and paper.
- It is possible to set up a local intranet such as that on the KLB school network. The web pages of information can be accessed only over the LAN. An intranet is free because it does not involve phone links.
- There is control over users’ access rights to programs and data.
Disadvantages of LANs:
- Printing can be slow. Where a lot of workstations are served by only one or two printers, long print queues may develop.
- A virus can spread more easily. If a virus gets into one computer, it is likely to spread quickly across the network because it will get into the central backing store.
- As data is shared there is a greater need for security. Users of the network have to have authentication techniques such as user ids and passwords. Unique user ID’s control access to the files and settings on the network while passwords prevent unauthorised users from logging onto the network. Data may also have to be encrypted so that it is meaningless if intercepted.
- If the server fails, all the workstations are affected. Work stored on shared hard disk drives will not be accessible and it will not be possible to use network printers either.
- The cost of installing the equipment is greater. Cabling can be expensive to buy and to install.
- Damage to cables can isolate computers. Some sections of the network can become isolated and will not be able to communicate with the rest of the network.
- Because networks can be complicated to maintain, a network manager may be need to be employed to run the system.
More Examples of LAN
Here are the examples of LAN:
- Networking in home, office.
- Networking between two computers.
- Wi-Fi (When we consider wireless LAN)
Local area network is the network which is made within the office, room or building.
For example in an office there are 5 computers. One computer is for secretary and it has printer attached to her computer. Now that printer can be shared to other computers by networking. This type of networking is called local area network. One computer may also be used to store large files and other computers can access these files through network. The network is made by connecting cables from all computers to a single device which has ports in it.
There are different technologies used to connect local area network:-
- Bus technology
- Ring technology
- Star technology
There are other types of network technologies also like mesh technology.
In bus technology all the computers are connected to single wire also called a bus. If any computer in the network stops working then others computers can still share files and data between them. Bus this technology is oldest technology used in networking.
In ring technology the computers are connected with each other in ring or circle form. For example one computer connects to each computer on both sides. If one computer wants to send file to destination that is not near it than this file is transferred through residing computers and so on.
Star technology is just like ring technology but it has a device called switch in center that is connected to all the computers in the ring. The other computers are connected to switch through hub. So if one hub (computer) wants to transfer data to other hub (computer) then it sends data to switch and then switch transfer that data to the destination hub.
Learn more: Two Types of Networks: LANs and WANs



















































































































